Customer interaction is any exchange between a business and its customers across all touchpoints—phone, email, chat, social media, website, and in-person—throughout the customer journey. This comprehensive guide explains what customer interaction means, the different types of interactions, practical examples across industries, and proven strategies for improving interaction quality at scale.
This article is designed for customer experience leaders, support managers, operations teams, and business owners who need to understand and optimize how their organizations engage with customers. Process Shepherd, which specializes in guided workflow solutions for customer-facing teams, provides this practical framework for managing interactions effectively.
Customer interactions fall into four main categories: service and support, sales and transactions, informational guidance, and relationship building. Each type serves distinct purposes at different stages of the customer journey, from initial awareness through purchase, support, retention, and advocacy.
This guide covers the essential components of effective customer interaction: the channels and touchpoints where interactions occur, skills teams need to deliver quality experiences, metrics for measuring interaction effectiveness, tools and technology that enable consistency, and best practices for continuous improvement. Whether you’re building a customer interaction strategy from scratch or optimizing existing approaches, this article provides actionable insights for creating interactions that build loyalty and drive business results.
What Is Customer Interaction?
Customer interaction is any exchange or touchpoint between a business and its customers across all channels—including phone, email, chat, social media, website, and in-person—throughout the customer journey. These interactions encompass every communication and engagement opportunity where customers connect with your brand, whether they’re asking questions, making purchases, seeking support, or providing feedback.
The purpose of customer interaction extends beyond simply completing transactions or answering questions. Effective interactions build trust through consistent, reliable experiences, create loyalty by making customers feel valued and understood, drive satisfaction by resolving issues and meeting needs effectively, and generate advocacy by turning satisfied customers into brand promoters who recommend your business to others.
Customer interactions occur throughout distinct stages of the customer journey. During awareness and consideration, interactions introduce your brand and help prospects evaluate options. At the purchase stage, interactions facilitate transactions and address buying concerns. Post-purchase support interactions resolve issues and answer product questions. Retention interactions maintain ongoing relationships through proactive engagement. Advocacy interactions turn loyal customers into vocal supporters who refer others and provide testimonials.
Each interaction, regardless of channel or stage, represents an opportunity to either strengthen or weaken your customer relationship. A single negative interaction can undo months of positive experiences, while consistently excellent interactions compound to create lasting loyalty and competitive advantage.
Types of Customer Interactions
Customer interactions fall into several categories based on their primary purpose and the channels through which they occur.
Digital Customer Interactions
Digital interactions happen through your website and online platforms. Website interactions include browsing product pages, using search functionality, and navigating your digital experience. Chatbot conversations provide automated assistance for common questions and simple requests. Email support handles detailed inquiries requiring documented responses. Support forms collect structured information about issues or requests. Self-service portals allow customers to find answers, track orders, and manage accounts independently without requiring agent assistance.
Digital interactions offer convenience and 24/7 availability while creating detailed records of customer preferences and behaviors that inform future engagement strategies.
Phone & Call Center Interactions
Voice interactions through call centers remain critical for complex issues, urgent situations, and customers who prefer human conversation. Live agent calls provide personalized assistance for problems requiring discussion, empathy, or multi-step troubleshooting. IVR (Interactive Voice Response) systems route callers efficiently and handle simple requests through automated menus. Call center interactions typically address situations where customers need immediate help, have complicated questions, or face problems that digital channels haven’t resolved satisfactorily.
The personal nature of voice communication makes these interactions particularly impactful—positive phone experiences create strong loyalty while negative ones generate lasting frustration.
Social Media Customer Interactions
Social platforms serve as public customer interaction channels where responses are visible to broad audiences. Twitter support handles quick questions and public complaints requiring fast, visible resolution. Facebook and Instagram interactions respond to comments, messages, and posts mentioning your brand. LinkedIn engagement serves B2B customer interactions and professional community building.
Social media interactions demand particular attention because they’re public—how you respond to one customer influences how others perceive your brand’s responsiveness and values.
In-Person Customer Interactions
Face-to-face interactions in retail stores, service centers, or other physical locations provide rich, multi-sensory experiences. Retail customer service helps shoppers find products, answers questions, and processes transactions. Product demonstrations show features and benefits tangibly. In-person problem resolution addresses issues requiring physical inspection or hands-on assistance.
Physical interactions allow for non-verbal communication, relationship building, and personalized service that purely digital channels struggle to replicate.
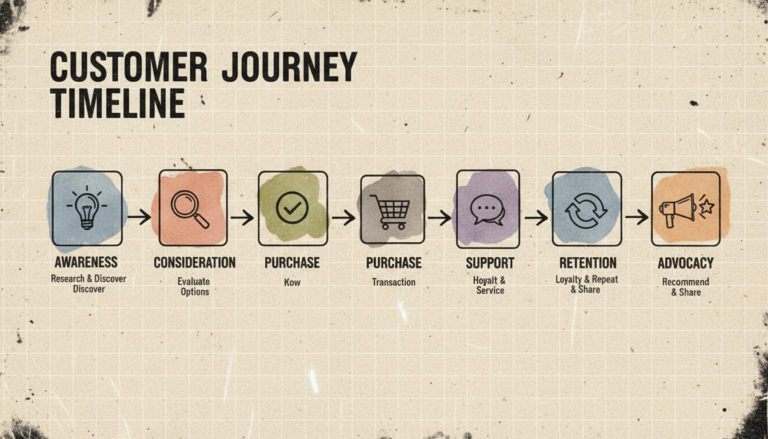
Customer Interaction in the Customer Journey
Interactions serve different purposes at various stages of the customer relationship, requiring adapted approaches for each phase.
Pre-Purchase Customer Interactions
Early-stage interactions introduce your brand and help prospects evaluate whether your solutions meet their needs. Marketing content interactions through blogs, videos, and social posts educate and build awareness. Website browsing interactions shape first impressions through design, navigation, and available information. Initial inquiry responses set expectations about responsiveness and helpfulness. These early interactions establish trust and credibility that determine whether prospects progress to purchase consideration.
Purchase & Sales Interactions
Transaction-stage interactions facilitate buying decisions and complete purchases. Sales consultations help customers choose appropriate products or services. Checkout assistance removes friction from payment and fulfilment processes. Upselling and cross-selling interactions recommend relevant additions that enhance value. Purchase confirmation interactions set expectations about delivery, onboarding, or next steps. These interactions directly impact conversion rates and initial customer satisfaction.
Post-Purchase Support Interactions
After-sale interactions resolve issues and answer questions that arise during product use. Technical support troubleshoots problems and guides customers through solutions. Returns and exchanges handle situations where products don’t meet expectations. Billing inquiries address questions about charges or payment issues. Onboarding assistance helps customers get started successfully with new products or services. These interactions significantly influence retention—excellent post-purchase support turns buyers into loyal customers while poor support drives churn.
Customer Retention Interactions
Ongoing relationship interactions maintain engagement and encourage continued business. Follow-up communications check satisfaction and offer additional assistance. Loyalty program interactions reward continued patronage and engagement. Personalized recommendations suggest relevant new offerings based on purchase history and preferences. Proactive outreach addresses potential issues before customers notice them. These interactions demonstrate ongoing commitment to customer success beyond initial transactions.
Customer Interaction Skills Every Team Needs
Regardless of channel or situation, certain fundamental skills determine interaction quality and customer satisfaction outcomes.
Active listening means fully concentrating on what customers say rather than just waiting to respond. It involves asking clarifying questions to ensure understanding, paraphrasing to confirm comprehension, and avoiding assumptions about what customers need. Active listening prevents miscommunication and shows customers they’re genuinely heard and understood.
Empathy demonstrates understanding of customer feelings and perspectives. It means acknowledging frustration when issues occur, recognizing the impact problems have on customers’ lives or businesses, and responding with genuine concern rather than defensive explanations. Empathy builds trust and defuses tension, particularly during challenging interactions.
Problem-solving delivers effective solutions quickly and confidently. It requires understanding issues fully before jumping to solutions, thinking creatively when standard approaches don’t apply, and following through completely to ensure resolution. Strong problem-solving creates satisfaction by actually helping rather than just processing interactions.
Clear communication conveys information customers can understand and act on. It means using plain language without jargon, explaining complex topics simply, confirming understanding before ending interactions, and setting accurate expectations about timelines and outcomes. Clear communication prevents confusion and repeat contacts caused by misunderstanding.
How to Improve Customer Interactions
Enhancing customer interaction quality requires systematic approaches that combine training, technology, and continuous measurement.
Use Customer Interaction Management Software
Comprehensive platforms centralize customer data, interaction history, and communication channels, giving agents complete context for every conversation. CRM systems store purchase history, preferences, and previous interactions so agents don’t ask customers to repeat information. Unified communication platforms route interactions appropriately and maintain conversation threads across channels. These systems prevent the frustrating experience of customers explaining situations repeatedly to different agents.
Implement Guided Workflows for Consistency
Structured workflows ensure agents handle similar situations consistently regardless of experience level or individual interpretation. Guided workflows present step-by-step direction during interactions, prompting agents to gather required information, follow proper procedures, and take appropriate actions based on customer responses. This consistency improves quality by standardizing execution of proven approaches rather than leaving outcomes to variable individual performance.
Process Shepherd provides this workflow guidance by turning procedures into interactive decision trees that adapt to specific customer situations, ensuring agents execute processes correctly during actual interactions rather than hoping they remember training perfectly under pressure.
Train Teams on Customer Interaction Best Practices
Ongoing training reinforces skills and introduces improved approaches based on performance data. Role-playing exercises practice handling difficult conversations in safe environments. Scenario-based training prepares agents for diverse situations they’ll encounter. Coaching based on actual interactions addresses specific improvement opportunities identified through quality monitoring. Regular skill refreshers prevent knowledge decay over time.
Measure Customer Interaction Quality
Systematic measurement reveals what’s working and where improvement is needed. Post-interaction surveys capture immediate customer feedback. Quality assurance reviews evaluate whether interactions meet standards. Performance analytics track key metrics across agents and teams. Regular measurement enables data-driven improvement rather than guessing about what needs attention.
Customer Interaction Metrics to Track
Several key metrics provide quantitative insight into interaction quality and effectiveness.
Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) measures how customers rate specific interactions, typically through post-contact surveys asking “How satisfied were you with your experience?” Scores reveal immediate perception of interaction quality and highlight agents or processes consistently generating high or low satisfaction.
First Contact Resolution (FCR) tracks the percentage of issues resolved during initial interactions without requiring follow-ups or escalations. High FCR indicates effective problem-solving and thorough handling. Low FCR suggests incomplete resolutions forcing customers to contact support multiple times, wasting their time and increasing operational costs.
Net Promoter Score (NPS) measures likelihood that customers would recommend your business to others, indicating overall relationship strength beyond individual interaction satisfaction. NPS reflects cumulative impact of all interactions rather than specific touchpoints.
Average Response Time measures how quickly customers receive replies across different channels. Fast response times demonstrate respect for customer time and create positive impressions, while slow responses generate frustration and negative perception.
Customer Effort Score (CES) assesses how easy or difficult customers found it to accomplish their goals during interactions. Low effort correlates strongly with loyalty—customers prefer businesses that make things easy rather than creating obstacles.
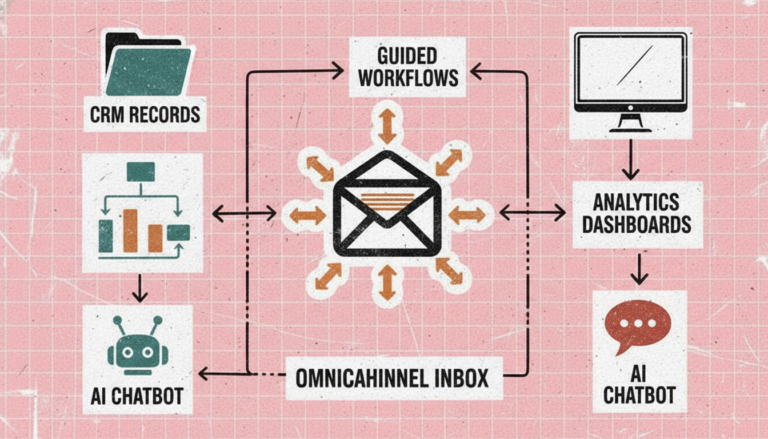
Customer Interaction Management: Tools and Technology
Technology platforms enable consistent, efficient, and personalized interactions at scale.
CRM systems like Salesforce, HubSpot, or Zoho centralize customer data, track interaction history, and provide unified views of customer relationships. They ensure agents have context about previous interactions, purchase history, and preferences before engaging with customers.
Guided workflow platforms like Process Shepherd direct agents through consistent processes during interactions. Rather than relying on memory or searching documentation, agents follow step-by-step guidance adapted to specific customer situations, ensuring quality execution of procedures every time.
AI chatbots handle routine questions and simple requests through automated conversations, providing instant responses outside business hours and deflecting volume from human agents. They work best for predictable scenarios with clear answers, escalating complex situations to humans appropriately.
Omnichannel platforms unify communication across email, chat, social media, phone, and other channels, maintaining conversation context when customers switch between channels and preventing repetitive information gathering.
Analytics tools measure interaction quality, identify improvement opportunities, and track performance trends, enabling continuous optimization based on data rather than intuition.
Benefits of Effective Customer Interactions
Quality interactions deliver measurable business value across multiple dimensions.
Increased customer loyalty emerges from consistently positive experiences that build trust and satisfaction. Loyal customers purchase more frequently, spend more per transaction, and remain customers longer, dramatically increasing lifetime value compared to customers with mediocre experiences.
Higher retention rates result when customers have no compelling reason to leave. Excellent interactions resolve issues satisfactorily, make customers feel valued, and create emotional connections beyond transactional relationships. Retention directly impacts profitability since acquiring new customers costs significantly more than retaining existing ones.
Improved revenue comes from loyal customers who buy more, accept upsells and cross-sells more readily, and provide valuable referrals that generate new customers at minimal acquisition cost. Quality interactions also reduce churn-related revenue loss.
Better operational efficiency occurs when interactions resolve issues correctly the first time, eliminating repeat contacts and reducing support costs. Streamlined interactions lower average handle time without sacrificing quality. Consistency reduces errors requiring costly correction.
Competitive differentiation develops when superior customer interaction becomes a brand hallmark that attracts customers away from competitors. In markets where products are similar, customer experience often determines purchasing decisions.
Customer Interaction Best Practices
Several proven practices enhance interaction quality consistently across teams and channels.
Personalize every interaction by using customer names, referencing previous interactions, acknowledging purchase history, and adapting communication style to individual preferences. Personalization shows customers they’re valued individuals rather than anonymous transactions.
Respond quickly across all channels whether customers contact you via phone, email, chat, or social media. Fast responses demonstrate respect for customer time and create positive impressions, while delayed responses generate frustration and negative perception.
Use data to understand customer history before engaging so agents have context about previous issues, purchases, preferences, and interaction patterns. Context prevents customers from repeating information and enables more relevant, helpful responses.
Empower agents with guided workflows that provide real-time direction during interactions, ensuring consistent execution of procedures without requiring agents to memorize every possible scenario. Workflows reduce errors and improve efficiency while maintaining quality.
Continuously measure and improve by tracking key metrics, analyzing patterns in customer feedback, identifying recurring issues, and implementing improvements based on data. Regular measurement reveals what’s working and what needs attention, enabling ongoing enhancement.
FAQs About Customer Interaction
What is customer interaction?
Customer interaction is any exchange or touchpoint between a business and its customers across all channels—including phone, email, chat, social media, website, and in-person—throughout the customer journey. These interactions encompass communications, transactions, support requests, and any engagement where customers connect with your brand.
What are the 4 types of customer interactions?
The four main types are: (1) Service and support interactions that resolve problems and answer questions, (2) Sales interactions that facilitate purchases and recommend products, (3) Informational interactions that educate and guide customers, and (4) Relationship interactions that maintain ongoing engagement and build loyalty. Each type serves different purposes throughout the customer journey.
How do you improve customer interactions?
Improve customer interactions by training teams on essential skills like empathy and active listening, implementing guided workflows for consistency, using customer interaction management software for context and efficiency, measuring quality through metrics like CSAT and FCR, and continuously refining approaches based on performance data and customer feedback.
What is customer interaction management?
Customer interaction management refers to the systems, processes, and strategies businesses use to handle, track, and optimize all customer touchpoints across channels. Call center experts use CRM platforms, communication tools, workflow systems, analytics capabilities, and the organizational approaches that ensure consistent, quality interactions throughout the customer journey.
Conclusion: Building Better Customer Interactions
Customer interaction quality determines whether your business builds loyal, enthusiastic customers or creates indifferent transactors who leave for competitors at the first opportunity. Every touchpoint—from initial website visits through purchases, support requests, and ongoing engagement—shapes customer perception and influences whether relationships strengthen or weaken over time.
Success requires more than good intentions about providing excellent service. It demands systematic approaches combining skilled people, proven processes, and appropriate technology that ensures consistency across thousands of daily interactions. Training develops essential skills. Guided workflows standardize execution. Technology provides context and efficiency. Measurement reveals what’s working and what needs improvement.
Organizations that treat customer interaction as strategic capability rather than operational necessity create competitive advantages that are difficult for rivals to replicate. When every interaction consistently demonstrates competence, empathy, and genuine commitment to customer success, loyalty and advocacy follow naturally, driving the retention and growth that superior customer experience enables.
Nola Neven
Nola Neven is a content strategist in the CX space, focused on turning complex operational problems into clear, credible content that people actually read, reference, and share.
Her work sits where content and operations meet. She spends her time understanding how contact centers and help desks really function day to day, where workflows break down, where teams rely on workarounds, and where systems quietly slow everything down.


